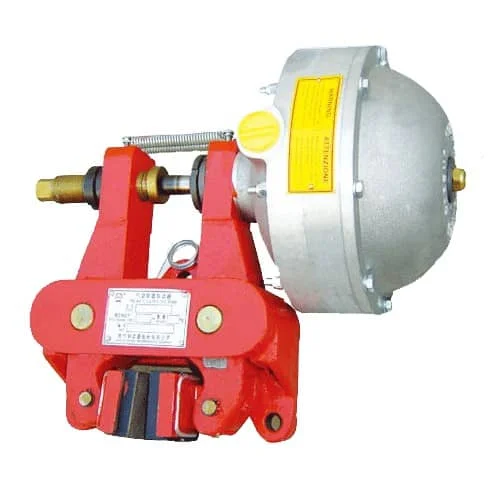
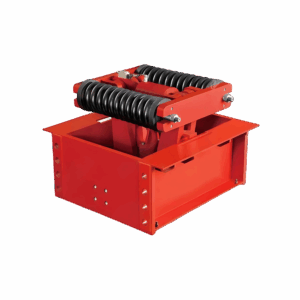
The QP series pneumatic caliper disc brakes are advanced mechanical components designed for braking and deceleration in various industries including lifting, transportation, metallurgy, mining, ports, and construction. They offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice for engineers and industrial applications.
Advantages
- Versatile Application: The QP series brakes are suitable for a wide range of applications due to their versatility in handling different environmental conditions and operational requirements. They can be used in harsh outdoor environments with rain, snow, or corrosive gases when specified as anti-corrosive models.
- Efficient Design: These brakes feature a simple, compact design that ensures easy installation and maintenance. Their lightweight structure facilitates integration into existing systems without significant modifications.
- Environmental Considerations: The brakes use asbestos-free brake pads, making them environmentally friendly. The pads are installed using a spring clip method, allowing for quick and easy replacement when worn.
- Adjustable Performance: Each specification within the QP series can accommodate adjustments to the braking torque, allowing for fine-tuning based on operational requirements. This adaptability makes them ideal for processes demanding precise control over braking.
- Integrated Systems: The QP series brakes can be connected to existing pneumatic systems without needing a separate power source, enhancing the efficiency and reducing installation complexity.
Application Range
The QP series is specifically tailored for mechanical systems that require reliable braking and deceleration. Industries such as heavy lifting, mining, and construction often utilize these brakes due to their robust performance and adaptability to varying operational conditions.
Operating Principle
- QP Series: Operates using spring brakes that are pneumatically released. This mechanism ensures that the brakes are engaged during power loss, providing safety in emergency situations.
- CQP Series: Functions oppositely with pneumatic brakes that are spring-released. This setup is optimal for systems that require a fail-safe design where the brakes are applied when pneumatic pressure is lost.
Usage Method
To use the QP series pneumatic caliper disc brakes effectively:
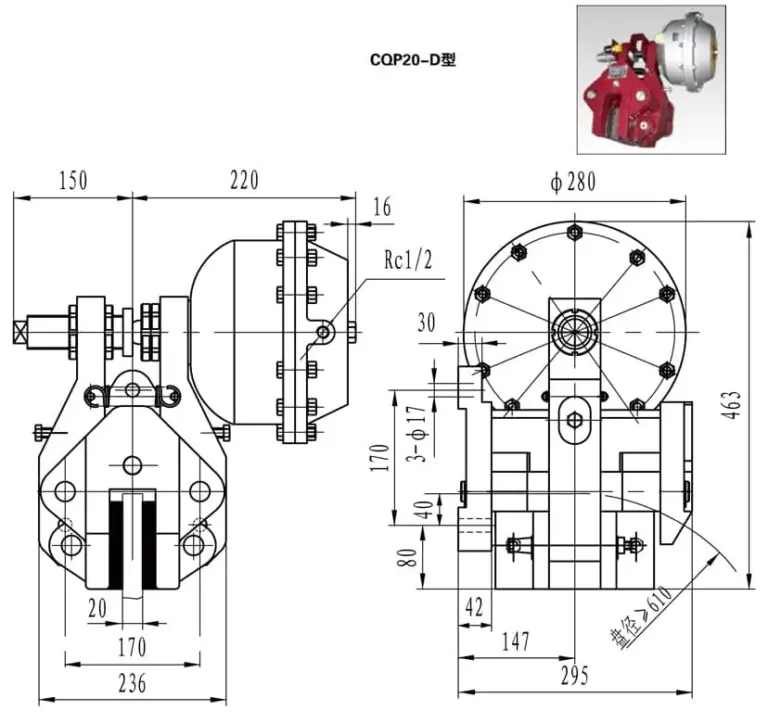
- Installation: Ensure the brakes are installed according to the provided dimensions and specifications. Models like the QP12.7-A, with a brake force of 6400 N and a radius adjustment of 0.03 m, should be securely mounted to achieve the desired torque, calculated as the product of rated brake force and effective radius.
- Adjustment: Adjust the braking torque to suit specific operational needs. For example, the QP30-D model can achieve a torque of 1400 Nm using 12 springs, offering significant braking power for heavy-duty applications.
- Maintenance: Regularly check the brake pads for wear and replace them using the spring clip method. This ensures consistent performance and prolongs the lifespan of the brakes.
- Environmental Adaptation: Select anti-corrosion models for outdoor use or environments with corrosive media. Ensure the air supply is clean, free of oil, water, and other impurities to maintain optimal brake function.
Important Considerations
- Working Pressure: The QP series operates within a pressure range of 5-7 bar, while the CQP series should not exceed 7 bar.
- Temperature Range: Suitable for environments with temperatures between -5℃ and 40℃.
- Model Specifics: Each model, such as the QP25.4-D, has specific dimensions and force ratings that should be adhered to for optimal performance. Adjustments in dimensions should be anticipated, as noted in the specifications.
In summary, the QP series pneumatic caliper disc brakes are a powerful, adaptable solution for industrial braking needs, offering environmental benefits, ease of maintenance, and efficient integration into existing systems. Their adjustable braking torque and robust design make them suitable for diverse applications across multiple industries.
Model Naming Convention
- Series Code (QP or CQP):
- Indicates the series of the brake, where “QP” is for standard spring brakes pneumatically released, and “CQP” is for pneumatic brakes spring released. If the model is vertical, an “L” is added, such as “CQPL.”
- Disc Thickness (mm):
- The number following the series code represents the thickness of the brake disc. For example, “12.7” indicates a disc thickness of 12.7 mm.
- Structure Type (Letter, often omitted):
- A letter that indicates the structure type. This part is typically omitted if not necessary.
- Air Bag Model (A, B, C, D):
- The letter after the first separator “-” indicates the type of air bag used.
- Spring Count (Omitted if standard):
- The number of springs used in the brake mechanism. This is included after the air bag model if it’s not the standard quantity.
- Air Bag Position (Left or Right):
- Indicates the installation position of the air bag with “Left” or “Right.”
- Special Requirements:
- Following the air bag position, special requirements are noted, such as “E1” for mechanical release indication or “E2” for sensor-based release.
Examples
- QP12.7-A-6Left:
- This indicates a QP series brake with a 12.7 mm disc thickness, A-type air bag, 6 springs, and left-side air bag installation.
- QPL12.7A-B-E1Right:
- This indicates a QPL series brake with a 12.7 mm disc thickness, B-type air bag, a mechanical release display, and right-side air bag installation.
This naming convention aids in precisely specifying the desired configuration and features for ordering and installation.
| Model | Rated Braking Force (N) | Effective Disc Radius (m) | Rated Torque (Nm) | Working Gas Volume (cm³) | Total Gas Volume (cm³) | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QP12.7-A | 6400 | 0.03 | Calculated Value | 273 | 553 | 24 |
| QP12.7-B | 4800 | 0.03 | Calculated Value | 140 | 293 | 20 |
| CQP12.7-A | 1788 x Working Pressure | 0.03 | Calculated Value | 273 | 553 | 23 |
| CQP12.7-B | 1055 x Working Pressure | 0.03 | Calculated Value | 140 | 293 | 19 |
| QPL12.7A-A | 6400 | 0.03 | Calculated Value | 273 | 553 | 24 |
| QPL12.7A-B | 4800 | 0.03 | Calculated Value | 140 | 293 | 20 |
| CQPL12.7A-A | 1788 x Working Pressure | 0.03 | Calculated Value | 273 | 553 | 23 |
| CQPL12.7A-B | 1055 x Working Pressure | 0.03 | Calculated Value | 140 | 293 | 19 |
| QPL12.7-B | 2100 | 0.03 | Calculated Value | 140 | 293 | 11 |
| CQPL12.7-B | 416 x Working Pressure | 0.03 | Calculated Value | 140 | 293 | 10 |
| QP30-D | 32800 | 0.065 | Calculated Value | 1400 | 3000 | 70 |
| CQP30-D | 6097 x Working Pressure | 0.065 | Calculated Value | 1400 | 3000 | 68 |
| CQP20-D | 6097 x Working Pressure | 0.065 | Calculated Value | 1400 | 3000 | 68 |
Notes:
- Rated Torque (Nm) is calculated as the product of rated braking force and effective disc radius.
- Working Pressure in CQP models is variable and affects the rated braking force.
- Specific installation dimensions and model variations may change, as noted in the specifications.
Drive
To ensure optimal performance and compatibility, the QP (CQP) series pneumatic caliper disc brakes should be paired with suitable pneumatic drive systems that match their operational requirements. Here are key considerations for selecting the right drive device:
Drive Device Compatibility
- Air Compressor System:
- The brakes require a pneumatic system capable of maintaining the necessary pressure range. For the QP series, a working pressure between 5-7 bar is needed, while the CQP series should not exceed 7 bar.
- The compressor should be able to deliver clean air, free of oil, water, and impurities, to ensure the brakes function effectively.
- Pressure Control and Regulation:
- A pressure regulator can help maintain consistent air pressure to the brakes, ensuring stable performance. This is particularly crucial for CQP models, where pressure influences braking force.
- Air Supply Lines:
- The pneumatic lines should be adequately sized to prevent pressure drops and ensure rapid response times. This includes using high-quality hoses and fittings that can withstand environmental conditions and mechanical stress.
- Valve Control System:
- Incorporating control valves, such as solenoid valves, allows precise control over brake engagement and release. This helps achieve adjustable braking times and smooth operation.
- Speed Control:
- Adding a speed control valve can help adjust the braking time, allowing for nuanced control over deceleration rates. This can be particularly useful in applications requiring variable speed control.
- Fail-Safe Mechanisms:
- For safety, ensure the pneumatic system includes fail-safe mechanisms that automatically engage the brakes in case of pressure loss, especially important for QP models with spring engagement.
By selecting drive devices that meet these criteria, the QP (CQP) series brakes can be effectively integrated into a wide range of industrial applications, ensuring reliability and performance.